electron configuration of calcium ion|How to Write the Electron Configuration for Calcium (Ca) : iloilo In this video we will write the electron configuration for Ca2+, the Calcium ion. We’ll also look at why Calcium forms a 2+ ion and how the electron configuration for Ca2+ is similar to the. Your Envato Account is a single username and password for all of Envato. Don't have an account? Sign up today.
electron configuration of calcium ion,In this video we will write the electron configuration for Ca2+, the Calcium ion. We’ll also look at why Calcium forms a 2+ ion and how the electron configuration for Ca2+ is similar to the.
The electronic configuration of cations is assigned by removing electrons first in the outermost p orbital, followed by the s orbital and finally the d orbitals (if any more .
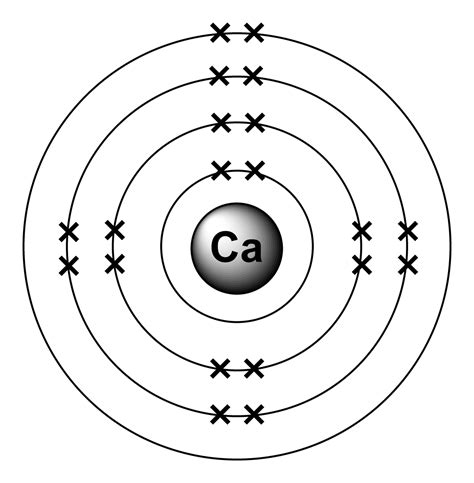
In order to write the Calcium electron configuration we first need to know the number of electrons for the Ca atom (there are 20 electrons). When we write the configuration . Calcium Electron Configuration - YouTube. Wayne Breslyn. 794K subscribers. Subscribed. 1K. 186K views 10 years ago. A step-by-step description of how to write the electron configuration.The electronic configuration describes how many electrons an atom or ion has and how they are arranged in the electron shells and subshells.For example, calcium is a group 2 element whose neutral atoms have 20 electrons and a ground state electron configuration of 1 s2 2 s2 2 p6 3 s2 3 p6 4 s2. When a Ca atom .
The calcium has two valence electrons in its outer shell. What is the Electron Configuration of Calcium. Calcium’s atomic number is 20 which means that in a neutral calcium atom, in its nucleus there are . The electronic configuration of cations is assigned by removing electrons first in the outermost p orbital, followed by the s orbital and finally the d orbitals (if any more electrons need to be removed).Electron Configurations of Ions. Ions are formed when atoms gain or lose electrons. Electronic structures of Cations. A cation (positively charged ion) forms when one or .The first three quantum numbers of an electron are n=1, l=0, m l =0. Only two electrons can correspond to these, which would be either m s = -1/2 or m s = +1/2. As we already know from our studies of quantum numbers . Calcium is the 20th element in the periodic table. It is a group 2 metal, also known as an alkaline-earth metal, and no populated d-orbital electrons. Calcium is the fifth most abundant element by .How to Write the Electron Configuration for Calcium (Ca) Here, the electron configuration of calcium ion(Ca 2+) is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6. This positive calcium ion(Ca 2+) has twenty protons, twenty neutrons, and eighteen electrons. Calcium ion: .electron configuration of calcium ion How to Write the Electron Configuration for Calcium (Ca) Here, the electron configuration of calcium ion(Ca 2+) is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6. This positive calcium ion(Ca 2+) has twenty protons, twenty neutrons, and eighteen electrons. Calcium ion: . Ca: [Ar] 4s^2 Calcium has an atomic number of 20. Simply use this information to obtain its electronic configuration. Thus, Ca: 1s^2 2s^2 2p^6 3s^2 3p^6 4s^2 or simply Ca: [Ar] 4s^2.In order to write the Iron electron configuration we first need to know the number of electrons for the Fe atom (there are 26 electrons). Once we have the configuration for Fe, the ions are simple. When we write the configuration we'll put all 26 electrons in orbitals around the nucleus of the Iron atom.
Writing out the electron configuration tells us how the electrons in an atom or ion are arranged in their shells, subshells and orbitals; This can be done using the full electron configuration or the shorthand version. The full electron configuration describes the arrangement of all electrons from the 1s subshell up; The shorthand electron .
Electron atomic and molecular orbitals A Bohr diagram of lithium. In atomic physics and quantum chemistry, the electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals. [1] For example, the electron configuration of the neon atom is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6, meaning that the 1s, 2s, and .Khanmigo is now free for all US educators! Plan lessons, develop exit tickets, and so much more with our AI teaching assistant.

The electron configuration of the calcium ion is 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p6. When calcium forms an ion, it loses two electrons and creates the Ca2+ ion..Hence, potassium corresponds to Li and Na in its valence shell configuration. The next electron is added to complete the 4s subshell and calcium has an electron configuration of [Ar]4s 2. This gives calcium an outer-shell electron configuration corresponding to that of beryllium and magnesium.For example, calcium is a group 2 element whose neutral atoms have 20 electrons and a ground-state electron configuration of 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2. When a Ca atom loses both of its valence electrons, the result is a cation with 18 electrons, a 2+ charge, and an electron configuration of 1 s 2 2 s 2 2 p 6 3 s 2 3 p 6 .Which atom in the ground state has the same electron configuration as a calcium ion, #Ca^(2+)# in the ground state? Question #a5631. An element with an electron configuration of #1s^2 2s^2 2p^6 3s^1# will have . When d-block (first row) elements form ions, the 4s electrons are lost first. Example \(\PageIndex{1}\): Iron . So rather than working out the electronic structure of scandium by imagining that you just throw another electron into a calcium atom, with the electron going into a 3d orbital because the 4s is already full, you really need to look .

Example of Determining Energy Levels (n) For example, if we want to determine the electron configuration for Cobalt (Co) at ground state, we would first look at the row number, which is 4 according to the periodic table below; meaning n = 4 for the s-orbital.In addition, since we know that the energy level for the d orbital is "n-1", therefore . The next electron is added to complete the 4s subshell and calcium has an electron configuration of [Ar]4s 2. This gives calcium an outer-shell electron configuration corresponding to that of beryllium and magnesium. . Electron Configurations of Ions. We have seen that ions are formed when atoms gain or lose .
The next electron is added to complete the 4s subshell and calcium has an electron configuration of [Ar]4s 2. This gives calcium an outer-shell electron configuration corresponding to that of beryllium and magnesium. . Electron Configurations of Ions. We have seen that ions are formed when atoms gain or lose electrons. A cation (positively .Similarly, the observed electron configuration of copper is [Ar]4s 1 3d 10 instead of [Ar]s 2 3d 9. The actual electron configuration may be rationalized in terms of an added stability associated with a half-filled (ns 1, np 3, nd 5, nf 7) or filled (ns 2, np 6, nd 10, nf 14) subshell. Given the small differences between higher energy levels . The third major category of elements arises when the distinguishing electron occupies an f subshell. The first example occurs in the case of the lanthanoids (elements having atomic numbers between 57 and 71).The lanthanoids have the general electron configuration [Kr]4d 10 4f i 5s 2 5p 6 5d 0 or 1 6s 2. where i is a number .
electron configuration of calcium ion|How to Write the Electron Configuration for Calcium (Ca)
PH0 · Identifying the Electronic Configuration of the Calcium Ion
PH1 · Identifying the Electronic Configuration of the Calcium
PH2 · How to Write the Electron Configuration for Calcium (Ca)
PH3 · Electron Configurations of Ions
PH4 · Electron Configuration for Calcium (Ca, Ca2+ ion)
PH5 · Electron Configuration for Calcium (Ca, Ca2+ ion)
PH6 · Electron Configuration
PH7 · Calcium Electron Configuration (Ca) with Orbital Diagram
PH8 · Calcium Electron Configuration
PH9 · Ca 2+ Electron Configuration (Calcium Ion)
PH10 · 9.6: Electron Configurations of Ions
PH11 · 7.4: Electron Configurations of Ions